Introduction
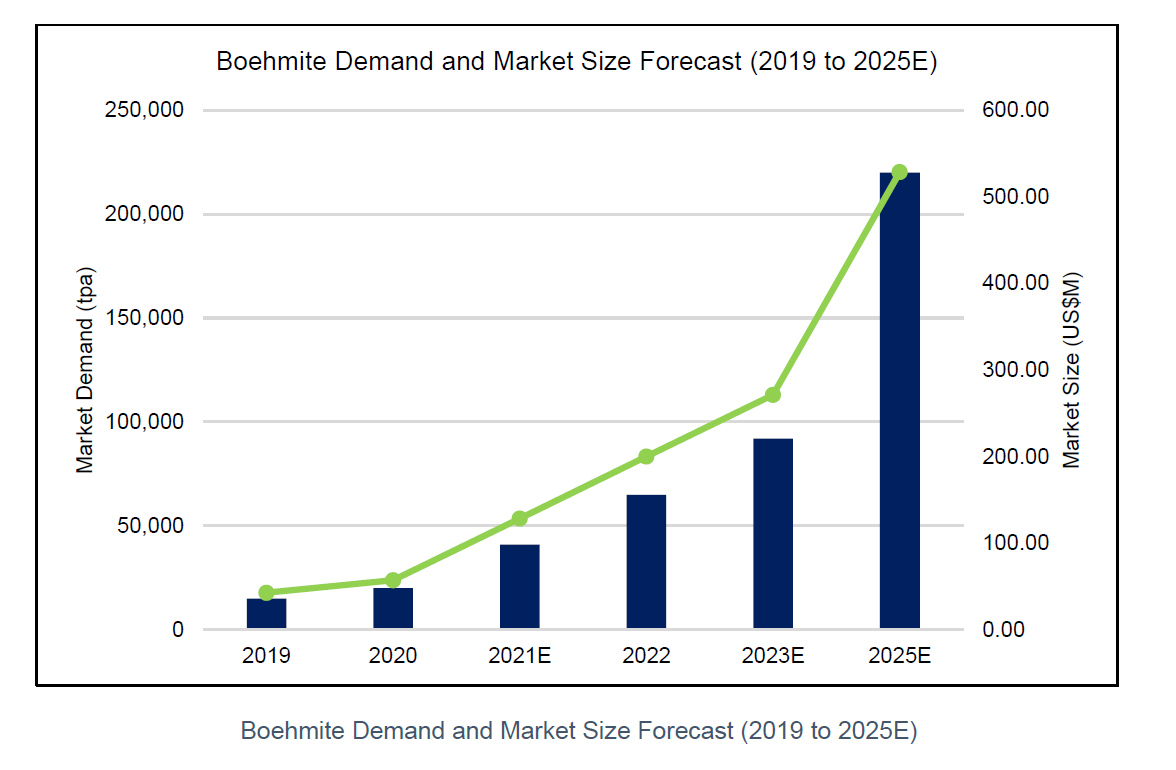
Boehmite is considered to be a next-generation inorganic coating material used in lithium-ion battery separators. Of which, the separator is a major component of lithium-ion batteries used in electric vehicles, energy storage, and consumer electronics. It is estimated that the global market size will reach US$528 million by 2025, up from US$42 million in 2019.
Product Features
Boehmite is an aluminium oxyhydroxide, white in appearance and characterised by its high purity level and narrow particle size distribution. It has excellent electrochemical stability, insulation, and heat resistance making it a good next-generation coating material for lithium-ion battery separators. When compared to high purity alumina, boehmite competes on thickness, pore structure, porosity, ionic conductivity, wettability, chemical and electrochemical stability.
Main Advantages of Boehmite
Compared with traditional high purity alumina coating material, it has the following advantages:
- Less absorbent making it easier to maintain the dryness of the separator. The content of water-soluble Na+ of boehmite at 0.002% is lower than that of alumina at 0.036%. The water absorption rate of boehmite is only half of that of high-purity alumina. Of which, is beneficial to the moisture control of high-nickel batteries and further improves the safety performance of batteries.
- The particle size distribution is narrower, the specific surface area is controllable, and the specific gravity is low, which is beneficial to improve the energy density. The specific gravity of boehmite is 3.05g/cm3, which is lower than the 3.90g/cm3 of alumina. The same weight of boehmite has 25% more coating area than alumina, which is beneficial to improve energy density. The application of boehmite will significantly reduce the total weight of the ceramic coating and the manufacturing cost of lithium-ion batteries.
- Narrow particle size distribution, good monodispersity, and regular morphology. When used as a separator coating material, the coating thickness is uniform, there are no excessively large and small particles, and the internal resistance is small.
- The coating film has better mechanical properties. The lithium-ion battery separator needs to have a certain mechanical strength to prevent safety problems caused by the failure of the separator. The polyethylene separator coated with boehmite has higher tensile strength than the polyethylene separator coated with alumina. In addition, the separator coated also has better puncture strength.
- Better thermal stability, mainly because the boehmite ion coating and the matrix separator have better interfacial bonding force, so that the boehmite coating acts as a supporting framework to resist the melting shrinkage of the polyethylene film at high temperature.
Other Advantages of Boehmite
- The hardness is lower than that of alumina, which reduces equipment wear and the risk of impurities brought in during processing. The Mohs hardness of alumina is 9, while the Mohs hardness of boehmite is 3.5. The gravure roll coating process is a commonly used. Boehmite can prolong the service life of the separator coating roller and the finished separator cutting knife by 3 to 4 times, reducing the impact on production and processing equipment. It also greatly reduces the risk of magnetic foreign matter being introduced in the production and processing steps, improving product quality and production efficiency.
- Boehmite has lower energy consumption and the production process is more environmentally friendly. High-purity alumina undergoes a series of complex processes such as calcination, pulverisation, and classification. Taking the hydrothermal method as an example, boehmite is placed in a high-temperature and high-pressure reactor for dissolution and recrystallisation, washing, drying and other processes, to prepare powder.
Contact us to purchase the full report today
Click to view the Table of Contents

Further reading
Our comprehensive battery mineral research reports include a brief introduction, industry chain, product specifications, processing methods, raw material requirements, cash cost analysis, pricing metrics, future industry development trends, and the competitive landscape. If you have specific reseach topics, reach out by email and contact us today to learn more.
You might be interested in our other battery mineral research reports
For Further Information