Introduction
Anode material is the negative electrode in high-performance rechargeable lithium-ion batteries and is paired with cathode in a lithium-ion cell. The anode acts as the host where it allows lithium-ion intercalation and deintercalation during the charge and discharge cycles. Moreover, the anode should have the lowest possible electrode potential, high Li+ migration rate, high Li+ intercalation/deintercalation reversibility, good electrical conductivity and thermodynamic stability.
Anode material generally needs to meet the following characteristics:
- Low first cycle irreversible loss
- High coulombic efficiency
- Fast lithium-ion diffusion into and out of the anode
- High ionic and electronic conductivity
- Minimum structural changes upon charge and discharge
- High specific capacity (mAh/g)
- Ability to form and maintain a stable solid electrolyte interface (SEI) layer upon cycling.
Product Categories
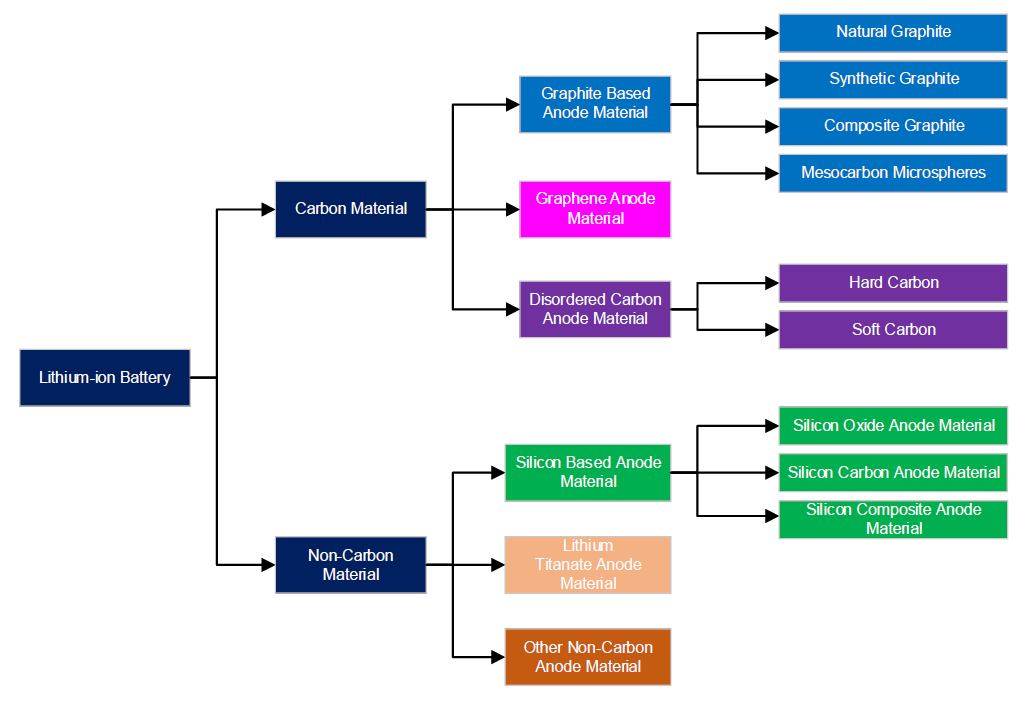
Products are mainly divided into two categories as either carbon-based or non-carbon based.
Carbon-based material is mainly subdivided into synthetic graphite anode material or natural graphite anode material. Other types include composite material, mesophase carbon microspheres, graphene-based material, and disordered carbon (hard carbon and soft carbon) material.
Non-carbon anode material is subdivided lithium titanate material, tin-based alloy material, silicon-based anode material, and other non-carbon anode material. At present, natural graphite and synthetic graphite anode material are most commonly used today.
Principal Production Methods
Natural graphite anode material uses natural flake graphite as the main raw material. Of which, this material has its own crystal structure and does not require graphitisation. Simply put, natural graphite anode material is made through crushing, spheroidisation, purification, surface treatment, and other processes.
Synthetic graphite anode material is made through a process called “graphitisation”. Of which, graphitisation is the structural change from disordered carbon atom structures towards a perfect three-dimensional crystal of pure graphite. Moreover, this process mainly involves heating non-graphitic carbon materials to a temperature above 2,800°C in a high-temperature electric furnace. Resulting in transforming the non-graphitic carbon material into an ordered graphite structure.
Mainstream incumbent graphitisation processing manufacturers use the crucible graphitisation processing method. Going forward, improving furnace loading efficiency is key to achieving cost reduction and differentiation for the incumbent graphitisation processing manufacturers.
Commercialisation
Global shipments of anode materials will reach 1.55 million tonnes in 2022, a year-on-year increase of 71.9%. China’s shipments of anode materials will reach 1.43 million tonnes in 2022, up 84.0% yoy.
Today, more than 90% of the world’s anode materials are produced in China. Of which, in 2022, China’s synthetic graphite shipments will be 1.15 million tonnes, accounting for 84%. Moreover, the natural graphite shipments will be 205,500 tonnes, accounting for 15%. Lastly shipments of other anode materials will be 14,000 tonnes, accounting for 1%.
The rapid development of the global new energy vehicle market led to a serious shortage of China’s mid-to-high-end anode materials in 2021-2022. In order to meet the downstream market demand for mid-to-high-end power batteries and keep pace with the capacity expansion of upstream and downstream leading power battery manufacturers, incumbent manufacturers expanded their production capacity one after another.
Moreover, with the gradual release of the expanded production capacity of various companies in 2021-2022, the market may shift from a shortage of supply to a balanced market, or even overcapacity in 2023.
Global production capacity reached 1.1 million tonnes in 2022, of which production capacity from Chinese manufacturers reached 940,000 tonnes, accounting for 85% of global production. Lastly production capacity of South Korea and Japan 160,000 tonnes is only expected to account for 15%.
Importance of ESG
Firstly, it should be noted, ESG considerations are becoming increasingly important in the synthetic graphite industry. Secondly, this is driven by a combination of investor and consumer demand, regulatory pressures, and environmental impact of synthetic graphite production. Lastly, companies in the sector are responding by adopting ESG policies and seeking to reduce their carbon footprint.

Competitive Landscape
Firstly, the Chinese material market is led by four major producers consisting of BTR New Material Group Co., Ltd, Shanghai Putailai New Energy Technology Co., Ltd subsidiary Sichuan Zichen Technology Co., Ltd, Ningbo Shanshan Co., Ltd, and Guangdong Kaijin New Energy Technology Co., Ltd. Moreover, these four producers had a combined market share exceeded 61.5% in 2022.
In addition, other major producers, include Shijiazhuang Shangtai Technology Co., Ltd (“Shangtai”), Hunan Zhongke Electric Co., Ltd (“Zhongke”), and Shenzhen XFH Technology Co., Ltd (“Xiangfenghua”). Moreover, these four producers had a combined market share exceeded 24.8% in 2022.
Lastly, outside of China, anode material production comes from South Korea and Japan, of which production is stagnated at around 53,000 tonnes. However, with a renewed interest in anode material, planned production capacity expansion coming out of these two markets is 261,000 tonnes per annum.
Contact us to purchase the full report today
Click to view the Table of Contents

What is driving the growth of the global anode material industry?
1. Increasing demand for anode material used in lithium-ion batteries applicable for electric vehicles and consumer electronics.
2. There have been significant advancements in lithium-ion battery technology, in particular, the commercialisation of high-end synthetic graphite anode material.
3. Low-carbon and low-energy manufacturing techniques are being developed for more ESG friendly synthetic graphite anode material.
4. Adoption of silicon-based anode material which can store a significantly higher amount of lithium ions compared to graphite.
Is ESG important for synthetic graphite anode material?
ESG is important for synthetic graphite anode material as its a key component material in lithium-ion batteries powering the decarbonisation of the global economy:
1. Incorporating ESG policies in the graphite market is slowly developing with greater emphasis on the upstream and midstream production.
2. ESG is growing among investors and consumers to differentiate between investing in or purchasing products from companies.
3. Synthetic graphite anode production can be over four times more carbon intensive than natural graphite anode production, due to its high-energy requirements during production and the use of fossil fuels in raw materials.
4. Most European anode plants are scheduled to use natural flake graphite as a raw material due its ESG advantages, mainly due to fewer greenhouse gas emissions.
Further reading
Our comprehensive battery mineral research reports include a brief introduction, industry chain, product specifications, processing methods, raw material requirements, cash cost analysis, pricing metrics, future industry development trends, and the competitive landscape. Lastly, if you have specific reseach topics, reach out by email and contact us today to learn more.
You might be interested in our other battery mineral research reports
For Further Information