Introduction
Graphene is a hexagonal two-dimensional carbon nanomaterial composed of carbon atoms as an element and sp2 hybrid orbitals. At present, Its shape can be divided into single-layer and multi-layer.
Graphene Characteristics
- High conductivity: theoretical carrier mobility at room temperature can reach 200,000 cm2/(V.s), which is 140 times that of silicon
- Thermal conductivity: thermal conductivity reaches 5,300W/(mK), higher than carbon nanotubes and diamond
- High strength: fracture strength is 42N/m, which is 100 times that of steel
- Highly flexible: bending does not affect its performance.
- Permeability: carbon six-ring structure, high density, helium (He) cannot penetrate, and the pores can be modified
- Translucency: single layer graphene absorbs only 2.3% of visible and infrared light
Principal Production Methods
Today, it can be produced using CVD method, physical stripping, mechanical stripping, and many other menthods:
- Micro mechanical stripping method
- Extensional growth method
- Chemical vapor deposition method
- Chemical oxidation-reduction method
- Carbon nanotube cutting method
- Solution stripping method
Moreover, according to the number of layers, graphene can be divided into single-layer, double-layer and multi-layer graphene:
- Single-layer graphene: refers to a two-dimensional carbon composed of a layer of carbon atoms that are periodically packed closely in a benzene ring structure.
- Double-layer graphene: refers to a two-dimensional carbon material composed of two layers of carbon atoms closely packed periodically in a benzene ring structure in different stacking modes.
- Multi-layer graphene: refers to a material composed of 3-10 It is a two-dimensional carbon material composed of carbon atoms that are closely packed periodically in a benzene ring structure in different stacking modes.
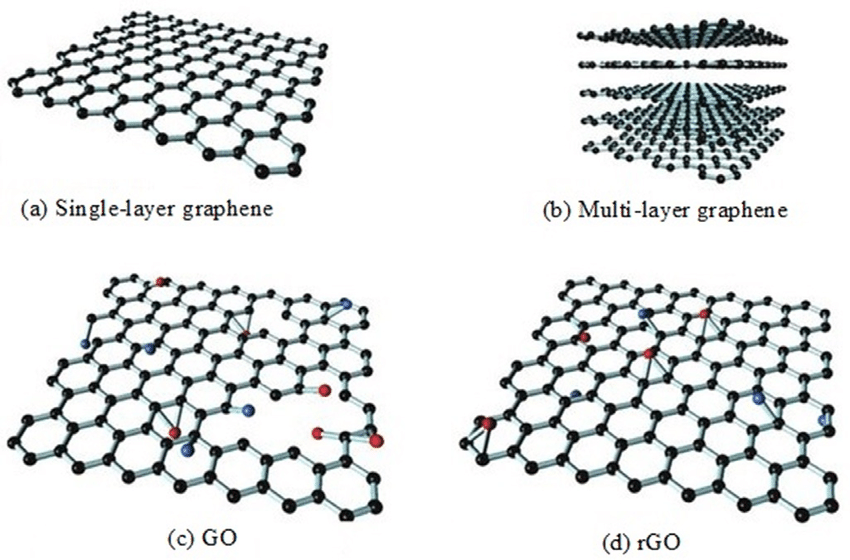
Firstly, different layers of graphene have different physical, chemical and mechanical properties. Moreover, the structure of single-layer graphene is relatively simple, and carriers show a linear dispersion relationship. Finally, the structures of double-layer and multi-layer graphene are more complex, with nonlinear and overlapping phenomena.
Graphene Applications
Today, countries such as China, South Korea, United States, and Japan continue to increase their investment in graphene research, leading to rapid advances in graphene technology.
Most importantly, today graphene is used throughout the new economy in fields including but not limited to semiconductor chips, conductive agents, sensors, lithium-ion batteries, cooling components, thermal conductive components, mechanical structures, flexible materials, wearable devices, curved screens, filter membranes, anti-corrosion coatings, seawater desalination, and transparent conductive film.
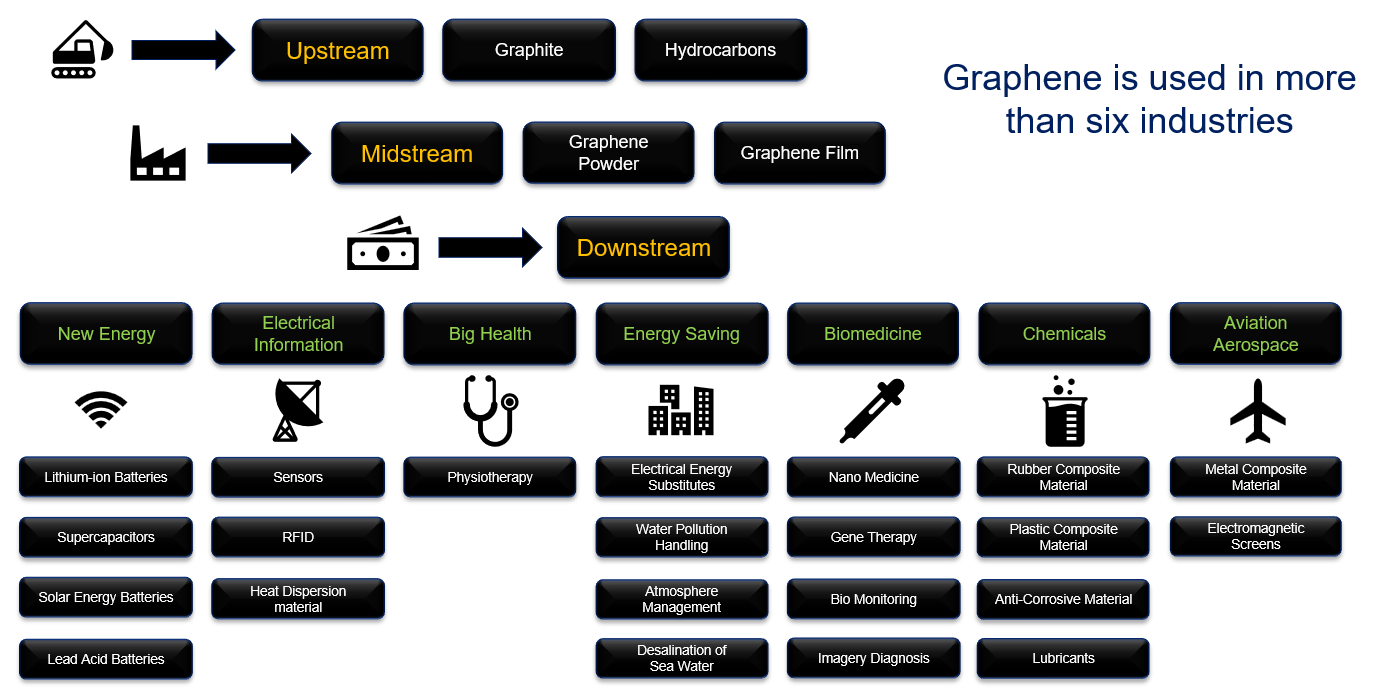
At present, commercial applications are wide, including anticorrosive coatings, petrochemicals, railways, highway bridges, conductive coatings, mobile communication antennas, radar radiation protection, building insulation coatings, heating cement, petrochemicals, marine antifouling coatings, nanocomposite antifouling coatings, ship antifouling bottoms, polymerization material, cement waterproof coating, tunnel, flame retardant coating, physical isolation layer, and nuclear power plants.
Commercialisation
Notably, the world continues to increase investment and attention in graphene. Since the advent of graphene in the laboratory in 2004, graphene-related research and commercial applications have continued to increase globally.
Most importantly, in terms of policy, many countries around the world have established graphene industry research and development funds and related support policies. Moreover, it can be seen that the research and development and industrialization of graphene have received great attention and attention around the world.
Global Landscape
Notably, many countries around the world have strategically laid out the graphene industry. Interestingly, in terms of funding, the United States announced an investment plan of approximately US$33 million from the National Science Foundation as early as 2008. Secondly, South Korea’s former Ministry of Knowledge Economy provided a total of US$250 million in support from 2012 to 2018. Moreover, the EU’s Graphene Flagship Plan signed in 2013 US$54 million was invested in the first phase. Finally, in China, the total investment in the graphene manufacturing innovation center established in 2017 has exceeded US$170 million.
Europe: Interestingly, the EU’s research on graphene started early and is highly systematic. Furthermore, the government has strong financial support for graphene. Moreover, it has launched the Graphene Flagship Program, which is the largest research program in the history of Europe.
China: Most importantly, China is a major exporter of graphene. The government attaches great importance to the development of graphene. Moreover, in 2015, it proposed a ten-year graphene development plan, clarifying the graphene industry scale goals of 10 billion in 2020 and 100 billion in 2025.
United States: Research has been carried out at the national level since 2008, led by the National Science Foundation, the Department of Energy, the Department of Defense and other institutions, focusing on supporting transistors, energy storage, supercapacitors, biotechnology and other fields
Japan and South Korea: Firstly, Japan has the most advanced graphene preparation technology in the world, and South Korea has a balanced graphene research and industrialization model. Secondly, the two markets are growing rapidly. Finally, on the government side, many well-known research universities such as Sungkyunkwan and Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology in South Korea, and the University of Tokyo in Japan have invested a lot of manpower and funds.
Competitive Landscape
Upstream: firstly, raw material graphene powder and film companies include Fangda Carbon New Material Co., Ltd, The Sixth Element (Changzhou) Materials Technology Co.,Ltd, China Baoan Group Co., Ltd, Air Liquide, Xiamen Knano Graphene Technology Co., Ltd, and DER.
Midstream: Secondly, graphene producers include Morsh, The Sixth Element Inc., Xiamen Knano Graphene Technology Co., Ltd, Haoxin Technology, BTR Group, MX, eCarbon, and 2D Carbon Graphite.
Downstream: Lastly, graphene producers of anti-corrosion materials, sensors, and composite materials include BTR Group, Xiamen Knano Graphene Technology Co., Ltd, Haoxin Technology, and Baotailong.
- Sixth Element (Changzhou) Materials Technology Co., Ltd: Established in November 2011, it is one of the largest producers of graphene powder in China.
- 2D Carbon Graphene Material Co., Ltd: Founded in December 2011, it focuses on the mass production of large-scale graphene transparent conductive film and tailored graphene nanoplatelets masterbatches for polymer modifications.
- Nanjing XFNANO Materials Tech Co., Ltd: This company is involved in the production of graphene and is a significant player in the graphene industry in China.
- Haoxin Technology Co., Ltd: This company is known for its production of graphene composite materials and has a 10,000-ton slurry production line for FLG (few-layer graphene) production.
- Carbonene Co., Ltd: A leading provider of graphene technology solutions with a comprehensive partnership with the Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Contact us to purchase the full report today
Click to view the Table of Contents
Further reading
Our research reports include an introduction, industry chain, product specifications, processing methods, raw material requirements, cash cost analysis, pricing metrics, future industry development trends, and the competitive landscape. Reach out by email and contact us today to learn more.
You might be interested in our other battery mineral research reports
For Further Information