Introduction
Lithium hexafluorophosphate is an inorganic compound with chemical formula LiPF6. The main use of lithium hexafluorophosphate is as the salt used in the electrolyte in lithium-ion batteries which are used in used in new energy vehicles, energy storage, and consumer electronics.
Specifically, the non-aqueous solutions of lithium hexafluorophosphate in carbonate solvents (e.g., ethylene carbonate (EC), dimethyl carbonate (DMC), diethyl carbonate (DEC) and/or ethyl methyl carbonate (EMC), with a small amount of one or many additives such as fluoroethylene carbonate and vinylene carbonate, serve as electrolytes in lithium-ion batteries.
Lithium hexafluorophosphate is currently the lithium salt with the best comprehensive performance, and it is also the most widely used commercial lithium salt.
The performance requirements of the lithium salt include:
- The lithium chemical salt has high solubility in organic solvents, and the degree of association is small and easy to dissociate, so as to ensure that the electrolyte has a high ionic conductivity. The ionic conductivity of the electrolyte can reach 7.2-11.5 ms/cm.
- Wide electrochemical window, the maximum voltage can reach 5V, which is higher than the 4.5V requirement of lithium-ion batteries.
- Facilitates the formation of SEI film on the anode.
- High stability, and no chemical reaction with electrode active materials and current collectors. Excellent anti-corrosion nature toward aluminium current collector of the cathode.
- Thermal stability, the best stable temperature range is -40 to 60oC, ensuring the safety of the electrolyte.
- Environmentally friendly, decomposition products.
- It is scalable and has cost-effective preparative processes developed in industry.
Commercialisation
Before 2011, the global lithium hexafluorophosphate was mainly dominated by three Japanese companies, Morita Chemical Industries Co., Ltd, Rising Chemicals (Stella Chemifa Corporation), and Kanto Denka Kogyo Co., Ltd.
Tianjin Chemical Research and Design Institute was the first to develop lithium hexafluorophosphate in China. It started the research on lithium hexafluorophosphate electrolyte for the first time in China in 1996, and completed a 4 t/a pilot plant in 1999. In 2005, it was approved by Tianjin Jinniu Power Material Industry Chemical for the construction of 80 tonnes/year lithium hexafluorophosphate construction project and a production capacity of 500 tonnes/year by 2010.
By 2013, Chinese domestic manufacturers, like Tianci Materials and Duofuoduo, achieved technological breakthroughs and rapidly expanded lithium hexafluorophosphate production capacity. From 2009 to 2015, China production capacity increased from 320 tonnes/year to 14,000 tonnes/year.
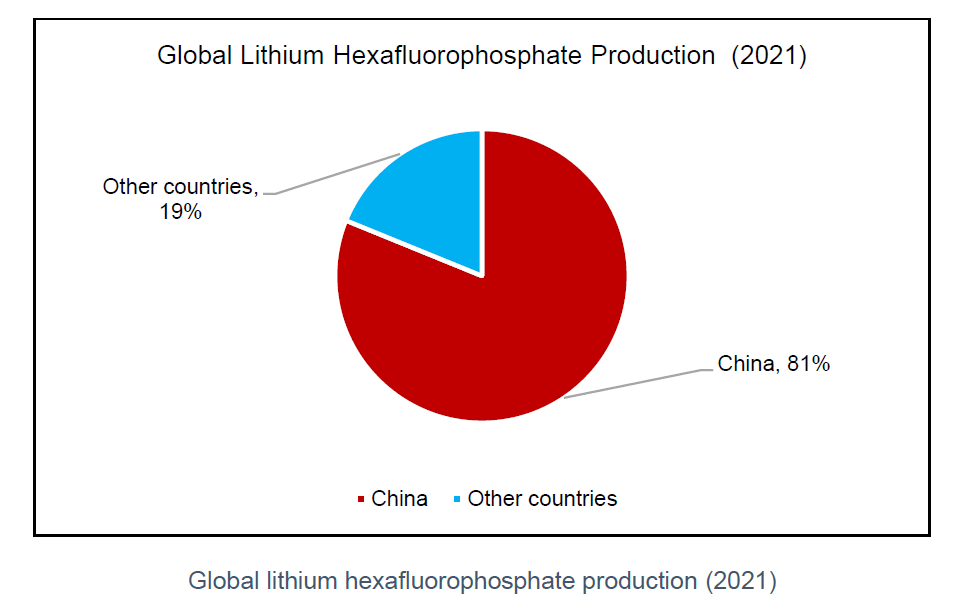
In 2021, China’s LiPF6 production capacity and output was 99,900 tonnes and 75,000 tonnes respectively. Major producers were Tianci Materials with a 34.6% market share and Duofuoduo with a 21.6% market share. With the commissioning of new projects, the output in 2022 has exceeded 120,000 tonnes while demand was about 103,800 tonnes.
Contact us to purchase the full report today
Click to view the Table of Contents

Further reading
Our comprehensive battery mineral research reports include a brief introduction, industry chain, product specifications, processing methods, raw material requirements, cash cost analysis, pricing metrics, future industry development trends, and the competitive landscape. If you have specific reseach topics, reach out by email and contact us today to learn more.
You might be interested in our other battery mineral research reports
For Further Information